PPPoA was a popular connection protocol used for connection between a network and its broadband users. The transition of networks to Ethernet established PPPoE as the successor of PPPoA. PPoE mainly connects BSR and the residential gateway.
How PPPoE Works
The first step of the process is the establishment of a PPPoE connection as per RFC2516. The second step of the process involves creating a link connection through Link Control Protocol (LCP) whose main purpose is to negotiate metrics such as authentication.
The third step of the process is to authenticate the subscriber using the Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP). Other authentication protocols that can be used include Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP). Finally, the IP addresses are assigned using Internet Protocol Control Protocol (IPCP). After these steps, the network is available to the subscriber.
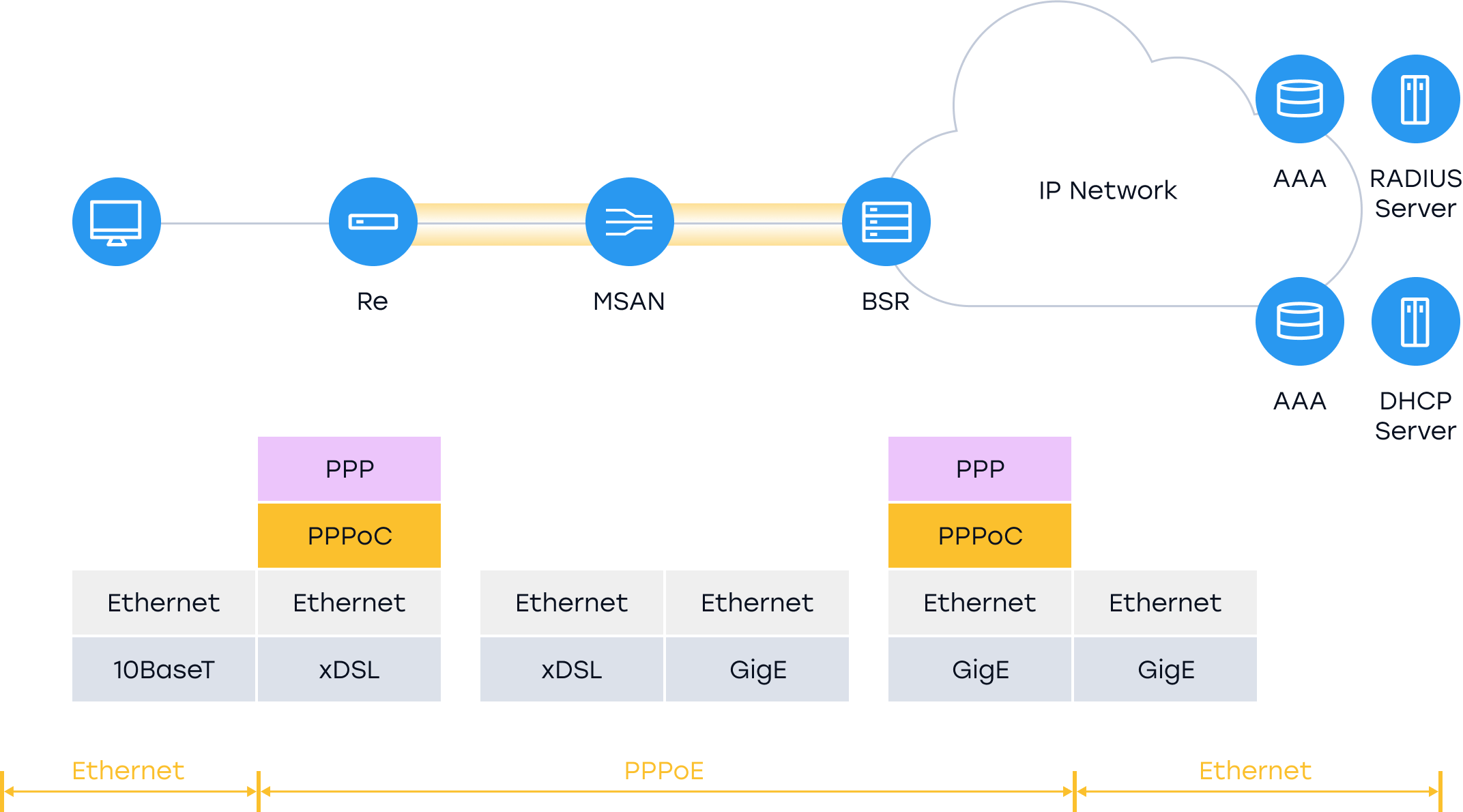
However, there is one more important aspect of the process; PPoE session monitoring. PPP has a protocol that is used for line quality monitoring. This function uses PPP keepalives to monitor the validity of sessions from both endpoints.
PPPoE Advantages
- PPPoE Supports retail and wholesale. There are two models of broadband networks including PPP Terminated Aggregation (PPP) and L2TP Access Aggregation (LAA). Retail services provided by network operators depend on PTA while LAA is used in transmitting network services through the wholesale model.
- Wholesale and retail combination.
- PPPoE offers a lot of room for scalability.
PPPoE Drawbacks
The main drawbacks of PPP are the use of two-level L2 encapsulation and support for unicast connections.
