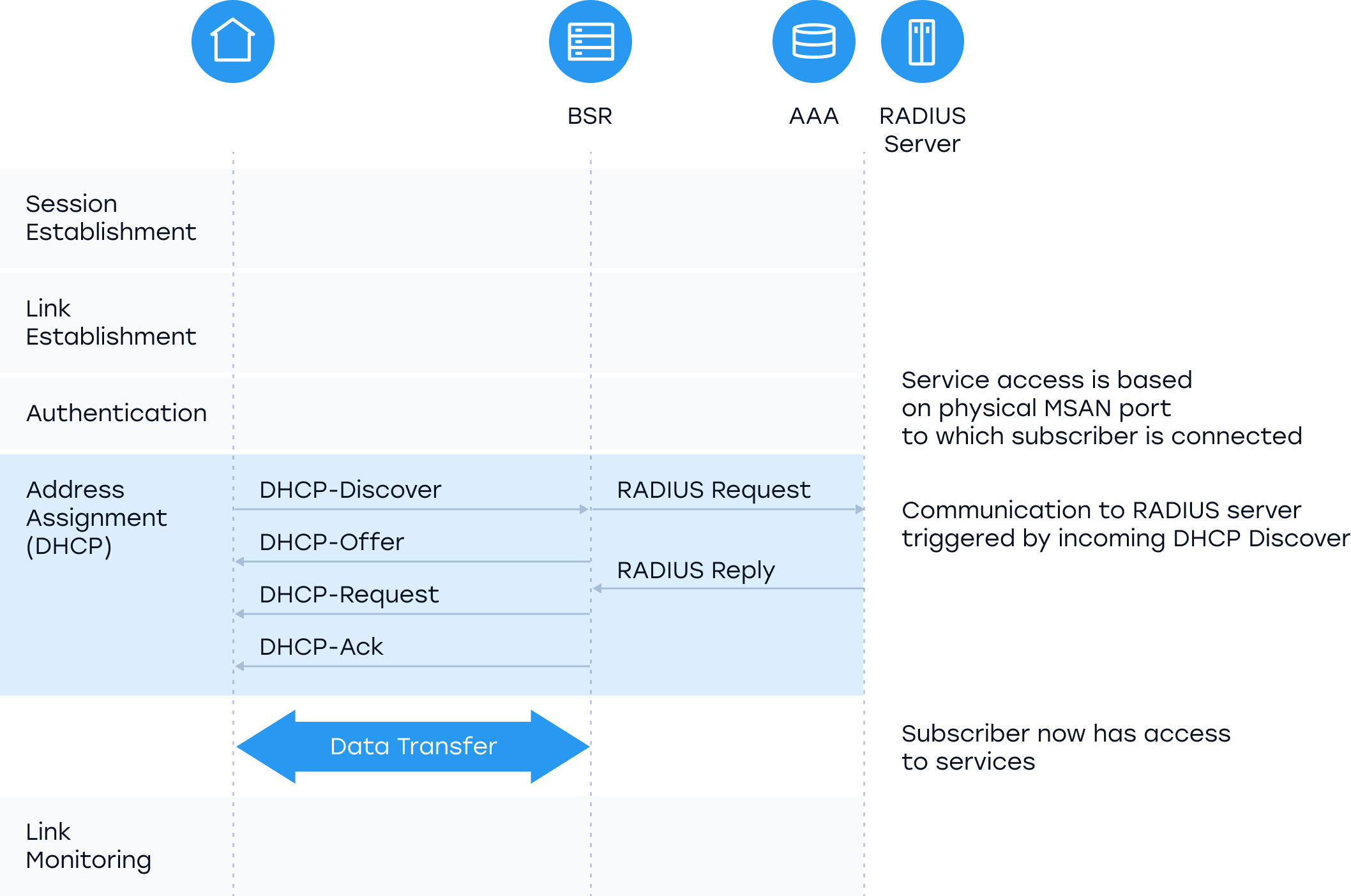
How IPoE Works (IPoE Process)
1. IPoE Session Establishment
Since IPoE is a connectionless protocol, it does not require link establishment and subscriber identification. Subscriber identification is done through the use of subscriber IP addresses.
2. IPoE Subscriber Authentication
Unlike PPPoE, IPoE lacks a subscriber login function but uses the subscriber’s physical connection to show services available including Ports, VLAN, etc.
3. IPoE Address Assignment
IPoE follows the classical DHCP mechanism; Discovery, Offer, Request, Acknowledgement (DORA). The process starts with the user sending a DHCP discovery message in the form of a broadcast. The DHCP server then offers a reply that includes an IP address. The third step is the user accepting one of the broadcast DHCP request messages sent by the servers. Finally, DHCP confirms the assignment of the address. However, the process is subjective to change depending on whether the DHCP server is located in another network.
4. IPoE Monitoring
The renewal process in IPoE is powered by the ability of the DHCP proxy relay to be used as a keep-alive mechanism. This is achieved by giving clients a short lease time.
IPoE Advantages
One of the major advantages of IPoE lies in its simplicity. IPoE is also economical when accessing the internet, and can support multicast broadcasting.
IPoE Drawbacks
The two main challenges facing IPoE are deeply rooted in its reliance on DHCP. IPoE therefore can therefore be difficult to support wholesale networks. IPoE also proves to be a threat to IPv6 migration.
PPoE Vs IPoE
The figure below gives a summary of the main difference between the two based on different metrics: