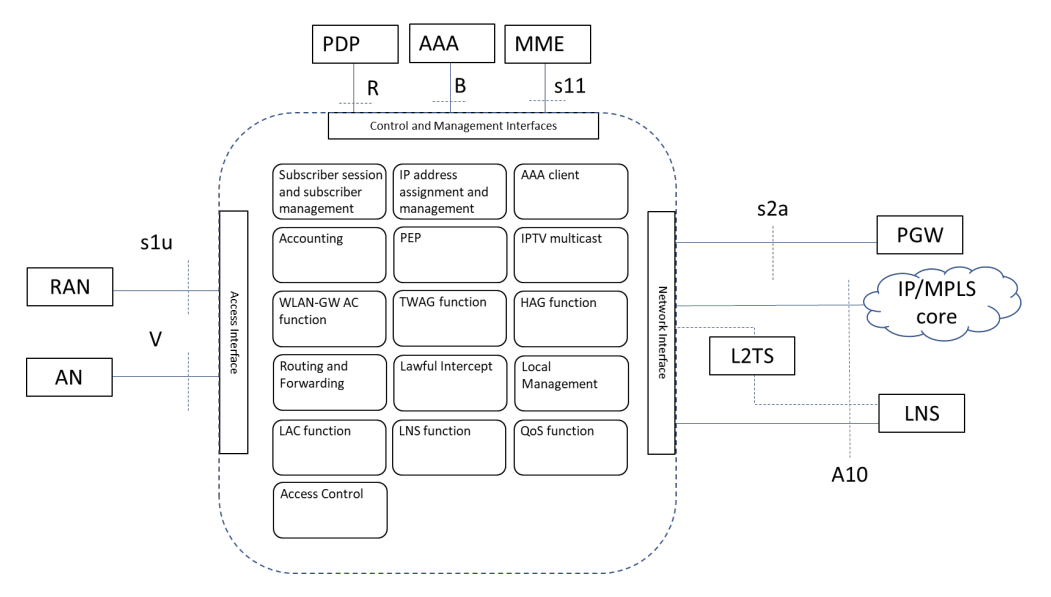
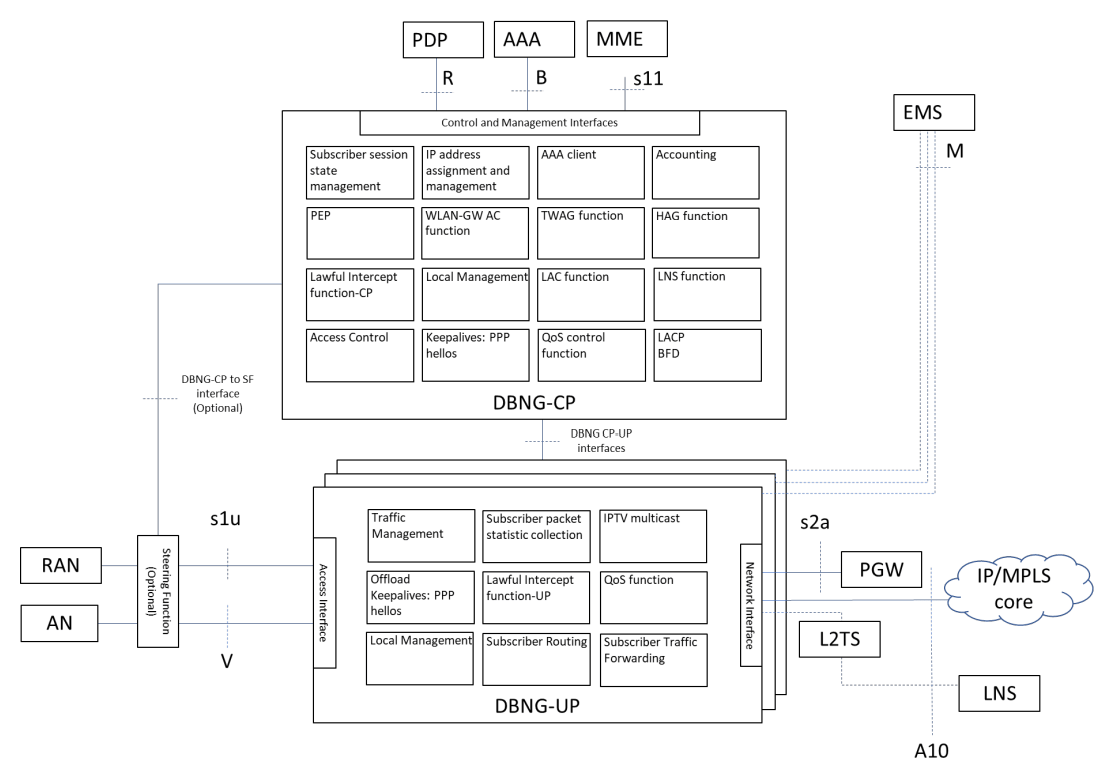
The Stingray SG concept supports the trend of the transition from the classic BNG device to the disaggregated BNG (DBNG) concept through the UP and CP separation. Let’s consider its benefits in more detail.
Multi-Service BNG
In the classic implementation of network infrastructure, a broadband service gateway is a multiservice device (Multi-Service BNG) that manages authorization, subscriber access to the Internet, authentication, bandwidth allocation, IP address allocation and accounting. With the development of Internet capabilities, the requirements are getting higher: adequate processing of the increasing volume of traffic is also necessary, taking into account the future growth of the Internet provider, and support for VoIP, IPTV, OTT, streaming video, gaming, and others.
For user experience, speed is important, and for control – the number of connected devices and integration interfaces. Because of this, it is necessary to determine in advance the necessary resources for MS-BNG, which can be used efficiently. This limits scaling and increases development costs.
Disaggregated BNG (DBNG)
To distribute the load and normalize the usage of the BNG device, the concept of disaggregated BNG (DBNG) has appeared. It involves the separation of control and user plane (CUPS) levels so that the architecture meets the increased number of subscribers and bandwidth requirements. CUPS also simplifies operation by supporting a single management interface on the CP to manage all UP.
Typically, the control level and the user level have different performance and scaling requirements: for the user level, the bandwidth for each user is important, and for the control level, the number of connected devices and integration interface requirements. In the case of MS-BNG, to process a large amount of traffic, it is necessary to make special hardware platforms that have a certain lifetime and limited development potential. Separation of control from traffic allows to allocate the necessary resources for maximum scaling and development of functionality.
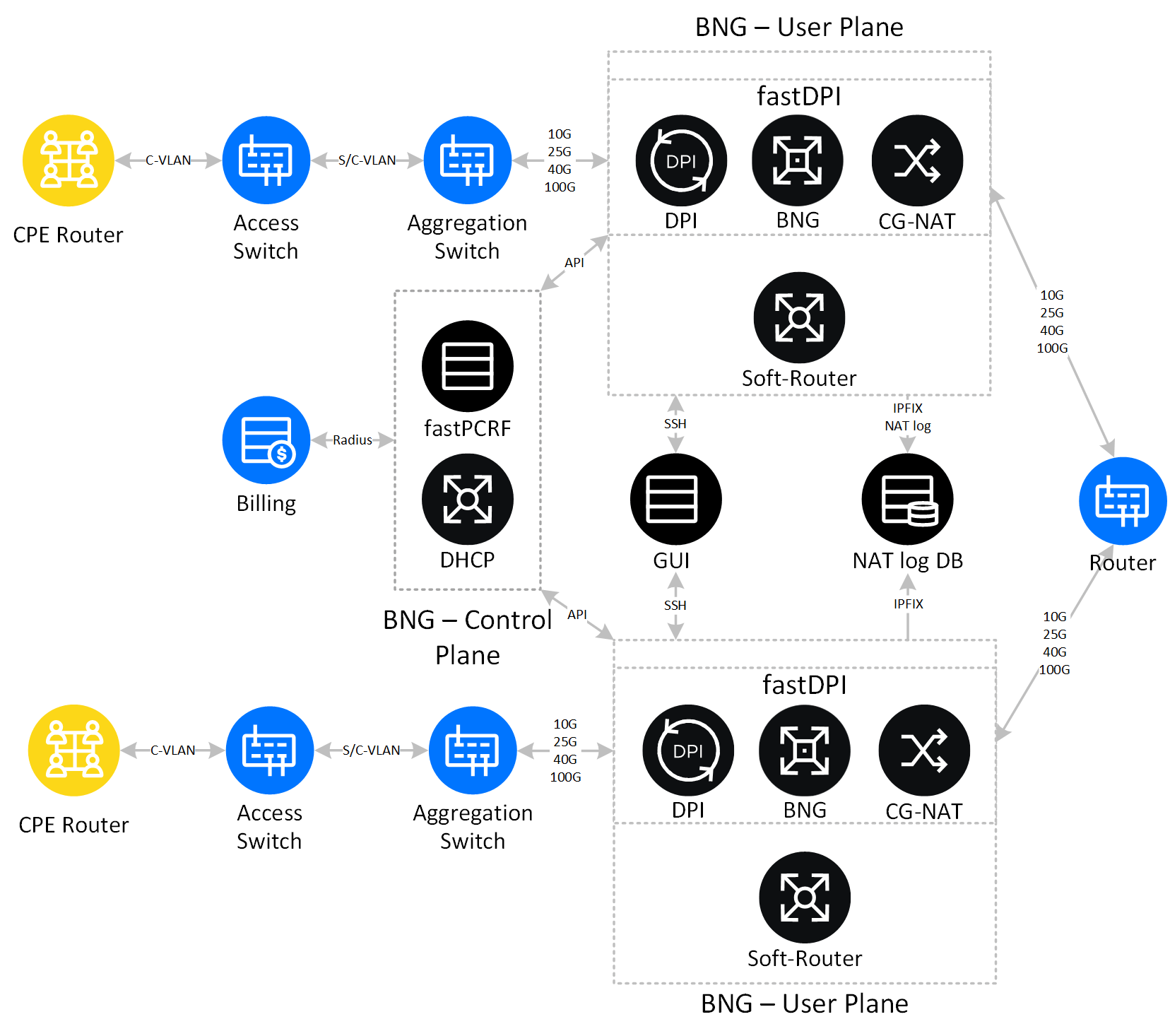
CUPS in VAS Experts products
The VAS Experts traffic monitoring and analysis system uses the fastDPI process in the User Plane role to perform the following tasks:
- Traffic Management
- Collection of statistics on subscriber traffic
- Applying QoS Policies
- Routing and Forwarding – BGP, OSFP
- Lawful Interception – Traffic mirroring
- Local management
In the Control Plane role, a fastPCRF process is used to perform the following tasks:
- Session Management of IPoE, PPPoE subscriber authentication
- AAA client – subscriber authorization, and authentication
- Accounting – subscriber traffic accounting
- Assigning and managing IP addresses – assigning IP addresses / prefixes via DHCPv4, DHCPv6
- WLAN-GW Access – Controller for access point management
We considered the main scenarios of BRAS components interaction from VAS Experts in the article about BRAS state diagram.