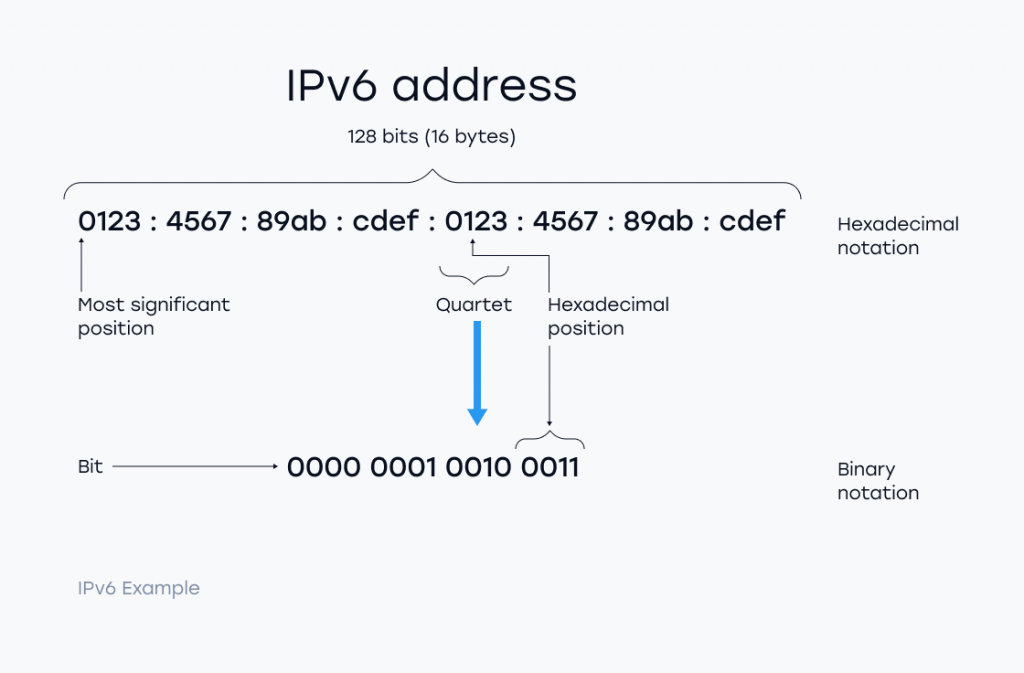
Unlike IPv4 which supports 4.3 billion addresses (32-bit address) IPv6 has the ability to support 2^128 IP addresses (340, 282, 366, 920, 938, 463, 463, 374, 607, 431, 768, 211, 456).
IPv6 addresses are expressed as 8 groups, of four hexadecimal values that are separated by colons.
IPv6 functionality
-
Extended address space
As stated earlier, IPv6 supports 128-bit (16-byte) source and destination IP addresses. This eliminates some middlemen technologies and mechanisms such as deployment NATs.
-
Simple Header Format
IPv6’s header has been made simple by moving options and unnecessary information (available in the IPv4 header), to the end of the IPv6 header.
-
Stateful address configuration and Stateless
By using both stateful and stateless configuration (absent DHCP server), and stateful (present DHCP server) it’s simple to configure hosts.
-
Built-In Security (IPSec)
IPv6 has enhanced security features compared to IPv4 because of its support for IPSec security.
-
Extensibility
This is among the main advantages of IPv6 as it provides extensibility to add information in an option part. Unlike IPv4, this protocol can be the same size as the packet itself.
-
Mobility
There are more devices in the world than there were when IPv4 was invented. IPv6 is built to support all these devices including IoT devices, mobile phones, etc. This is because of its ability to capitalize on extension headers and IP autoconfiguration.
IPv6 VS IPv4
| IPv4 | IPv6 |
| 32-bit addresses | 128-bit address |
| Unachievable end-to-end connection integrity | Achievable end to end connection integrity |
| Manual and DHCP address configuration support | Auto and renumbering address configuration support |
| Security feature depends on the application | In-Built IPSec security feature |
| Supports broadcast message transmission scheme | Available anycast and multicast message transmission |
| 20-60 bytes header capacity | 40 bytes fixed header |
| Checksum field available | Lack of Checksum field |
| Decimal address representation | Hexadecimal address representation |
| Uses Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) in MAC address mapping | Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) in MAC address mapping |
