
In addition, if at home each user can configure QoS on their router, then the telecom operator, using modern network equipment, manages the bandwidth for all its subscribers and provides consistently high quality for each of them.
What the Quality of Service (QoS) is
The Quality of Service (QoS) is a tool using which priorities are assigned for various types of traffic, and with the help of DPI systems even for certain applications, dividing bandwidth between them in different proportions. Properly configuring the QoS rules guarantees continuous online video playback while a large file is being downloaded, or fast web browsing while the OS is being updated in the background. The QoS is applicable to any technology that manages data traffic to reduce packet loss, latency and jitter in the network. The QoS monitors and manages network resources by prioritizing certain types of data on the network.
An internet connection can be compared to a hospital, in which bandwidth is the number of doctors to treat patients, patients are applications, and a nurse is a router that distributes them.
In an ordinary network, an indifferent nurse distributes patients evenly to free doctors, regardless of the complexity of the disease, whether it is a person with a bruised arm or a victim in a car accident with a concussion and broken bones. Each of them will be treated, but they will have to wait the same amount of time until there is an available doctor. If all patients are served with the same priority, sooner or later this will lead to disastrous consequences for the hospital and victims.
The same thing happens on the home network or the provider’s network. The bandwidth of the communication channel is distributed evenly within the data plan, without taking into account the importance of each application. For example, if you are talking on Skype, and at this time, your children launch a Netflix movie, the quality of the call will deteriorate dramatically. The Internet provider, in turn, is limited by the speed of the channel to the higher-level telecom operator, and its bandwidth may not be enough to ensure the quality of connection if all users simultaneously start downloading files through the torrent client at maximum speed.
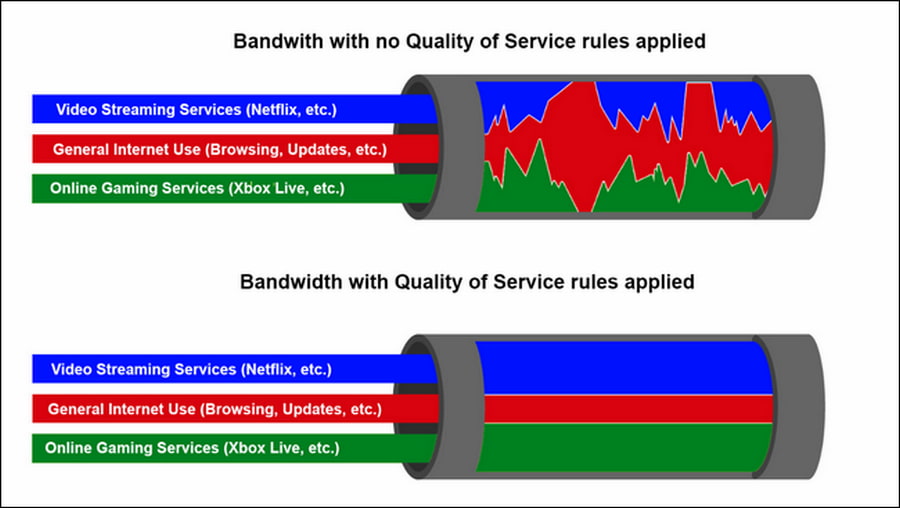
Turning to our comparison with the hospital, the quality of service is a competent nurse who distributes patients among doctors in the most effective way: several specialists will deal with the victims of an accident, and a patient with a bruise will wait for one doctor when they become available.
On a QoS network, the priority will be given to the application or service that you independently determine (online video, IPTV, online games, etc.), it will get high speed and minimal lags.
What Problems does QoS Solve?
The QoS helps to solve user problems when receiving traffic from various applications.
Packet loss
It occurs when network channels are congested, when routers and switches start losing packets. For example, during voice or video calls, there may be lags and speech breaks in sessions. Also, packets can be lost when the queue of packets waiting to be sent is full.
Jitter
The phase jitter of the digital signal is the result of network congestion, time bias, and route changes. Strong jitter can degrade the quality of communication, for example, while watching a video on YouTube or streaming a video on Twitch.
Latency
The time a packet takes to pass from the source to the destination should be as close to zero as possible. If an IP voice call has a high latency, users may have an echo and an overlaid sound.
How does QoS Work?
When subscribers use the Internet provider’s network to transfer information between network endpoints, the data is formatted into packets. Packets are a way of organizing information to transmit it over the network.
The QoS tools prioritize packets to maximize bandwidth utilization. The network can only transmit a certain amount of information for a specific period. Therefore, the QoS tools prioritize packets that ensure bandwidth utilization for the best internet service.
The QoS tools examine packet headers to determine their priorities. Packet headers are bits of information that tell you what the packet contains, the destination IP address, and what it will be used for. A QoS tool can read the packet header and determine that the packet is associated with streaming video, and give it priority over less time-sensitive data packets.
Advantages of QoS
The main advantage of the QoS is that it ensures the availability of applications running on the network. The QoS ensures secure data transmission over the network and allows operators to efficiently use existing bandwidth instead of upgrading the network infrastructure to increase bandwidth.
Other advantages of QoS:
- Access of critical applications to the network resources they need,
- Better traffic management,
- Cost optimization — a company does not need to purchase a new network infrastructure,
- Improved user experience.
QoS Implementation
There are hundreds of different routers – both for home and office, as well as complex carrier-class devices. Not every one of them has a QoS function, and if it does, then its implementation may differ in the range of possible settings. Some can only prioritize among devices, some can allocate certain types of traffic (for example, video or voice communication), DPI systems are able to recognize applications that do not use headers and data structures known beforehand for data exchange, make changes to the priority field of packets passing through it for further application of the QoS rules.
It is impossible to talk about the nuances of setting up each device, but it is possible to describe the basic steps to start using the QoS function to ensure a better quality of work with the Internet.
Step 1: Define the goal
Before you start setting up any device, you need to clearly define the goals of setting up the QoS. If you decide to set up a home router, then it can be the priority of a work computer over other devices with Internet access to ensure comfortable work, or the priority of online games over streaming video to ensure minimal latency and lags during the game.
In a home network, the rules should be selective and extremely simple. If you apply dozens of different priorities, you can get a negative result when none of the applications will work normally.
Telecom operator uses the QoS to achieve more global goals:
- Traffic differentiation
- Ensuring uniform traffic flow
- Guarantee of quality and speed of Internet access for each subscriber
- Preventing network congestion
- Reduction of Uplink costs.
But the principles of achieving them are similar to a home network: determining priority types of traffic and applications, setting up rules depending on priority and time of action.
Step 2: Determine the Internet speed
For a telecom operator, Internet speed is the speed of access to a higher provider (Uplink) or to several providers. This value is fixed and distributed among all subscribers according to their data plans. The task of its optimization and competent distribution should be solved by the QoS rules to ensure customer satisfaction with the service sourced.
The speed of the home Internet often does not match the provider’s stated speed for some reason, so determining its real figure is an important task before setting up the QoS. There are concepts of upload and download speeds that need to be determined independently.
To get real, you need to close all applications on your computer that create a load on the network, connect it to the router with a copper cable. Wi-Fi technology, especially if it does not work according to modern Wireless N or Wireless AC protocols, can be a bandwidth bottleneck. Measurements can show a speed of 40 Mb/s instead of the available 75 Mb/s specifically because of the limitations of the wireless data transfer speed.
Go to www.speedtest.net and click the Start button. The result should be converted from Mbit/s to Kbit/s, since the QoS settings are most often set in these units. This can be done by multiplying the values obtained by 1,000.
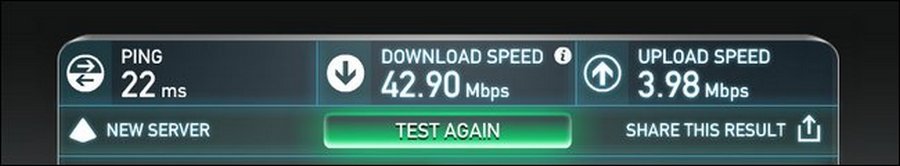
In this example, we got an download speed of 42,900 Kbit/s, and an upload speed of 3,980 Kbit/s. These values can be distributed between users and applications on the network.
Step 3: Enable QoS on the router
It is impossible to describe the order of enabling the QoS on all routers, since each manufacturer provides the user with its own management interface, and carrier-class network devices such as Cisco, Juniper, and Huawei are configured from the command line.
In most cases, you will need to go to the device management page (type its address in the browser, most often it is 192.168.1.1), enter the admin login and password specified in the user manual, and go to the NAT section of network settings, the QoS tab. Select Enable next to Start QoS, the port for applying the rules — WAN (connection port to the provider); the download and upload speed (downlink and uplink) should be specified in the amount of 85—90% of that measured in Step 2.
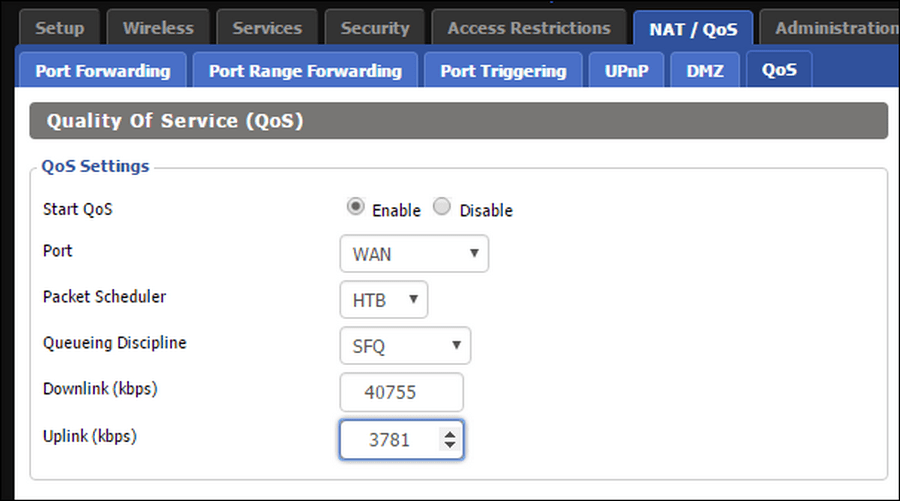
The lower speed is specified in order to give the QoS handler room to maneuver, so and in no other way it works efficiently. Now the quality of service is enabled and you need to configure the prioritization rules.
QoS Tools
Certain QoS mechanisms can manage the quality of data traffic and support the QoS requirements defined by the network administrator. The QoS mechanisms are divided into categories according to the functions they perform in network management.
- Classes and labels allow you to distinguish between applications and classify packets by traffic types. The labels indicate that each packet belongs to a network class that network devices recognize. Classification and labeling are implemented in network devices: routers, switches and access points.
- Congestion management. These tools use packet classification and labeling to determine which queue to put the packets in. Congestion management tools include priorities, first-in-first-out queues, and low-latency queues. Congestion should be avoided in order to monitor network traffic for congestion. The tool drops packets with low priority in case of congestion.
- Efficiency of channels. These tools allow you to maximize bandwidth utilization and reduce packet latency when accessing the network. Channel efficiency enhancement tools include real-time Transport Protocol (RtTP), Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), header and channel compression.
How to Prioritize Traffic
After the QoS function is enabled, it is necessary to determine the rules according to which it will work with traffic.
Telecom operators set up rules based on data obtained from DPI system analytics tools that show bandwidth bottlenecks and trends depending on the time of day. Some home devices have ready presets that the user should use to prioritize.
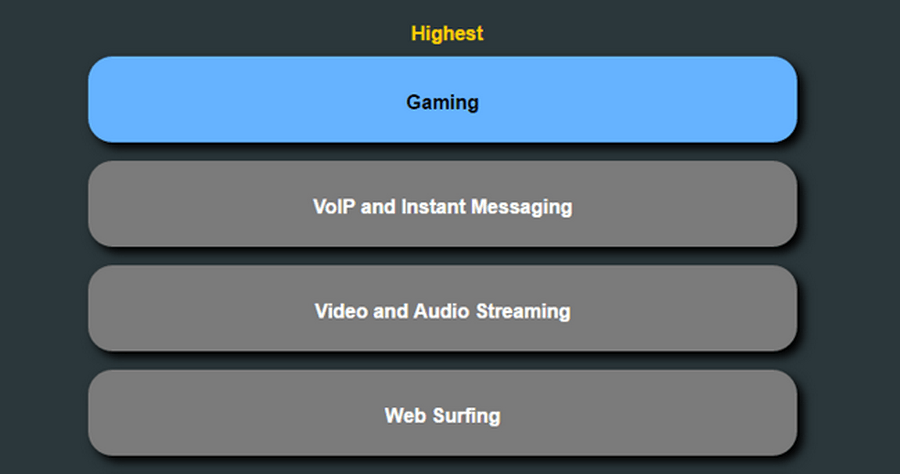
If the router allows manual priority settings, you need to set their fork points as a percentage of the total bandwidth:
- Maximum: 60–100%
- Premium: 25–100%
- Express: 10–100%
- Standard: 5–100%
- Bulk: 1–100%
These parameters determine the bandwidth value for a specific device or application. For example, by setting the Maximum for an application, you assign it to use 60% of the bandwidth if the network is loaded and 100% if the network is fully available. If you set the Bulk, then when the network is free, the application can use any bandwidth speed, but if there is a load, it will receive only 1%.
We would like to remind you that prioritization should be approached with a clear understanding of what you want to limit.
Prioritization Options
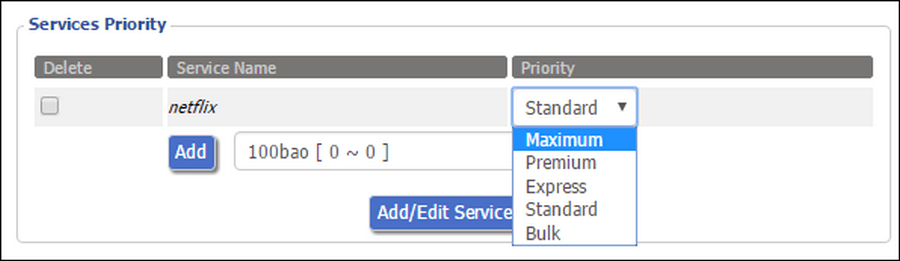
1. Priority of service or application
It allows you to assign the bandwidth priority of a particular application or service over the rest for any device on the network. For example, if it is necessary that Skype always has a dedicated bandwidth, and video and audio communication does not have any lags, distortions or artifacts.
2. Interface priority
The interface in this case is the method by which your devices connect to the network. You can set a higher priority for devices that are connected by wire or wireless network devices, or, conversely, degrade the priority of guest devices.
3. Priority of devices by IP address
You can assign a higher priority to a specific device on your network by its (static or reserved dynamic) IP address, thereby providing it with a higher access speed compared to others.
4. Priority of devices by MAC address
If you use dynamic addressing, you can still assign a high priority to one of the network devices by its MAC address, which is unique and information about which can be obtained either from the software or from the label on the case.
Test and Evaluation
The most important rules in setting up the QoS are to add rules sequentially in your own time. You need to start with the most significant, and then configure individual applications and services. If you have achieved the desired result and the QoS fulfills all your requirements, you need to save the configuration in the form of screenshots or a backup file in case you need to reset the router and restore the settings.
Setting up the QoS is a more complex process than the basic configuration of the router, and for a telecom operator there are also additional capital costs for the purchase of a DPI platform, however, the result will allow for better Internet access, as well as saving money on the purchase of a high-speed communication channel.
* — Source: www.howtogeek.com
