Key Technical Advantages of Migrating to IPv6
Unique IP Addresses
IPv6 enables each device to have a unique public IP address without the need for Network Address Translation (NAT). Previously, multiple devices shared a single public address, but now entire subnets can be allocated to each user, simplifying network operations and improving performance.
Improved Routing and Configuration
IPv6 streamlines routing and network configuration processes through built-in enhancements.
Enhanced Security
- Unique IP Address for Each Device: This makes internet connections more transparent, simplifying access management and monitoring.
- Built-In IPsec Support: Unlike IPv4, IPsec is an integral part of IPv6, providing data security at the protocol level.
These features make IPv6 not only more functional but also better suited for scalability and security in the modern Internet.
Current IPv6 Adoption Statistics
Overview of Global IPv6 Adoption
Despite its advantages, IPv6 adoption in many countries is gradual due to the widespread reliance on IPv4-based infrastructure, which requires time and resources to transition fully. Nevertheless, the number of IPv6 users has significantly increased in recent years. IPv6 is now actively utilized in areas such as mobile networks, the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud technologies.
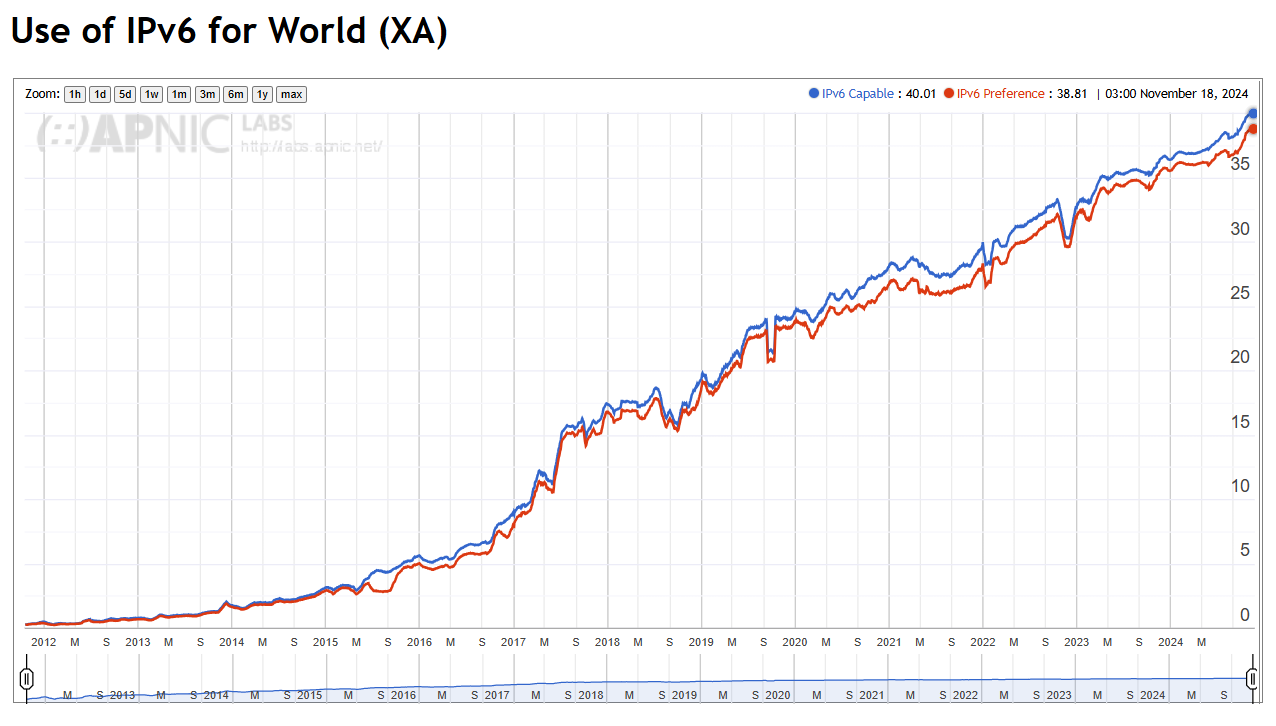
As of November 18, 2024 , 38.81% of global internet traffic is transmitted via IPv6, according to APNIC. This figure highlights the steady growth of IPv6 usage and its gradual establishment as the new standard. Support for IPv6 is expanding among providers and operators in regions experiencing high growth in new connections and devices, particularly with the development of next-generation mobile networks and IoT expansion.
APNIC collects and publishes IPv6 deployment statistics, including metrics for IPv6 Capable (potential IPv6 usage) and IPv6 Preferred (actual preference of IPv6 over IPv4).
Global IPv6 Adoption Trends Over the Last Decade (as of November 18, 2024)
Source: APNIC Stats (November 18, 2024)
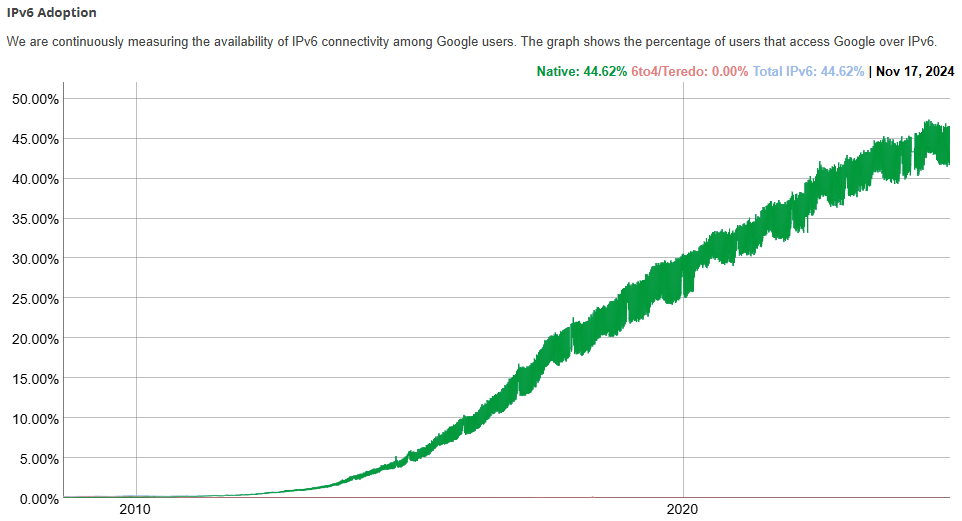
For a more comprehensive view, Google also provides IPv6 adoption data. As of November 2024, 44.62% of global IPv6 traffic is recorded, reflecting the share of users accessing Google services via IPv6.
Percentage of Users Accessing Google via IPv6 (as of November 17, 2024)
Source: Google IPv6 Statistics (November 17, 2024)
Top Countries Leading IPv6 Adoption (November 18, 2024)
- India: 82.24% of all internet traffic
- France: 69.94%
- Malaysia: 69.9%
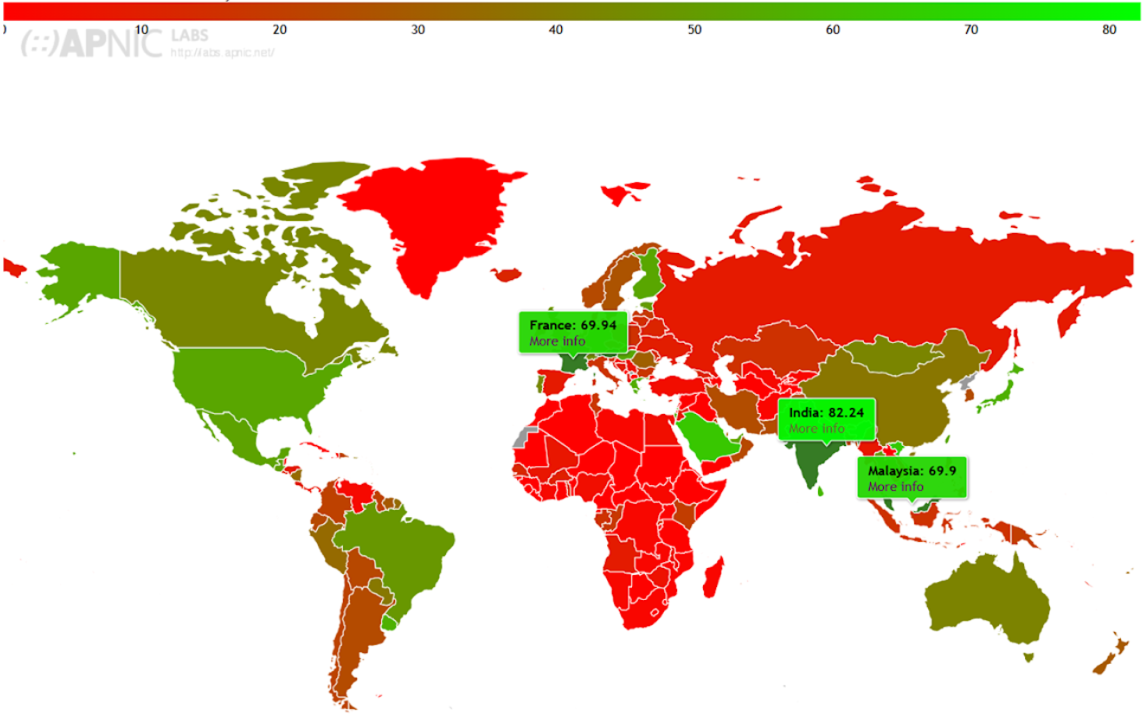
(Source: APNIC Stats)
Why IPv6 Traffic Dominates in These Countries
For instance, in India , this growth is largely attributed to Reliance Jio , which launched the country’s first all-IP LTE mobile network in 2016. From the start, Reliance Jio adopted IPv6, prompting other market players to recognize its advantages, particularly in addressing IPv4 exhaustion.
In Malaysia and France , the high share of IPv6 traffic is primarily due to the efforts of major telecom operators and the support and incentives provided by government and regulatory bodies.
Case Study: IPv6 Implementation at X-COM
In 2019, after nearly a year of preparation and testing, X-COM deployed IPv6 and DualStack IPv4/IPv6 support based on the SSG platform, giving subscribers access to the new protocol.
Steps in the IPv6 Implementation Process:
- Obtaining addresses from RIPE and network allocation.
- Network planning.
- Configuring BGP.
- Setting up DNS.
- Integrating with GGC (Google Global Cache).
- Configuring Radius.
Today, IPv6 is enabled by default for all X-COM subscribers. However, activation requires accessing the subscriber’s personal account. Currently, 21.3% of users have activated IPv6, but IPv6 traffic accounts for only 4.1% of total traffic.
The implementation of IPv6 had minimal impact on the workload of the operator’s technical support. Exceptions include rare cases related to IPv6 setup on the subscriber’s end or WAN port configuration on routers.
Challenges and Insights
Detecting resource availability has become more complex—some resources operate seamlessly, while others do not. Questions about IPv6 speed and scalability remain unresolved. Has IPv6 improved performance compared to IPv4? Likely not, but IPv4 also did not exhibit significant issues.
Future Transition to IPv6
“IPv6 traffic will continue to grow, and edge infrastructure will expand its support for the new protocol. However, no radical changes are expected. The proportions between IPv4 and IPv6 will gradually shift, but we won’t see revolutionary changes,” commented Roman Chuchuk, X-COM representative.
Conclusion
IPv6 is not just a new Internet protocol standard but a necessity driven by modern realities. IPv4’s limitations, such as address exhaustion and network complexity, make transitioning to IPv6 a crucial step for companies seeking stable network operations and readiness for future challenges. However, as the data suggests, IPv6 adoption is progressing steadily rather than rapidly, and a complete transition to the new protocol is still a distant goal.
Future Outlook: The Evolution of Network Technologies with IPv6 Growth
The world of networking will continue advancing toward broader IPv6 adoption. Increased IPv6 traffic and a gradual shift in the balance between IPv4 and IPv6 will enhance the global internet ecosystem. However, this process will be evolutionary rather than revolutionary. Organizations that begin implementing IPv6 today will gain a competitive advantage, preparing their networks for the growing number of connected devices and higher user demands.
VAS Experts offers proven solutions to help service providers adapt their networks for IPv6 with minimal costs. Our team provides a tailored approach and guidance on all aspects of the new protocol’s implementation, as well as on the capabilities of the SSG platform.