When a connection is established between BNG and Customer Premise Equipment (CPE), the subscriber can access broadband services provided by the Network Service Provider (NSP) or Internet Service Provider (ISP).
The other function of BRAS is to establish and manage subscribers sessions. When a session is active, BNG aggregates traffic from various subscriber sessions from an access network, and routes it to the network of the service provider. BRAS is deployed by the service provider and is present at the first aggregation point in the network, such as the edge router. With BRAS solution, an ISP can effectively manage subscriber access.
Subscriber management functions of BRAS:
- Authentication, Authorization and Accounting of subscribers’ sessions
- Address assignment
- Security
- Policy management with Quality of Service (QoS)
- Additional services
BRAS/BNG Architecture

The network architecture with the BRAS solution from VAS Experts includes the following components:
SSG (fastDPI) provides analysis and processing of traffic that passes through the platform, applying traffic policing and management. Through a combination of DPI technology, software BRAS/BNG and CG-NAT it solves such ISP’s challenges as:
- Traffic recognition by protocols with DPI technology
- Application of traffic policing to all subscribers or individually to some
- Application of platform services (CG-NAT, Allow Lists, Filtering by Block Lists, etc.)
- Export reports in various formats (NetFlow, IPFIX-clickstream, IPFIX-nat, IPFIX-flow, etc.)
- BRAS/BNG – NAS functions (Termination for IPoE, PPPoE, DHCP L2 subscribers).
DHCP server — a component which is responsible for issuing private addresses to subscribers. Any CentOS-compatible implementation can be used. The current implementation uses the Kea DHCP server.
Software router — a component that announces and receives routes via OSPF, BGP dynamic routing protocols. Possible to use any soft-router: BIRD, FRRouting, QUAGGA, Juniper CRPD etc.
PCRF provides the platform interaction with the operator’s OSS via the RADIUS protocol (AAA — Authentication, Authorization, Accounting).
- The fastDPI and PCRF components communicate with each other internally via a TCP/IP stack.
- The PCRF can be either hosted on a separate physical or virtual server or run on the same server together with an SSG.
- A single PCRF server can serve a cluster of several SSGs.
Subscribers session types
- IPoE DHCP subscriber session: The IP over Ethernet (IPoE) subscriber session is established using IP protocol that is used between the CPE and BNG; IP addressing is done by DHCP protocol.
- IPoE Static IP subscriber session: The IP over Ethernet (IPoE) subscriber session is established using IP protocol that is used between the CPE and BNG; IP addressing is Static conf.
- PPPoE subscriber session: The PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) subscriber session is established using the point-to-point (PPP) protocol that is used between the CPE and BNG.
Vendor Specific Attributes
Regular users
Parameters for Blocked (inactive) users sending by CoA
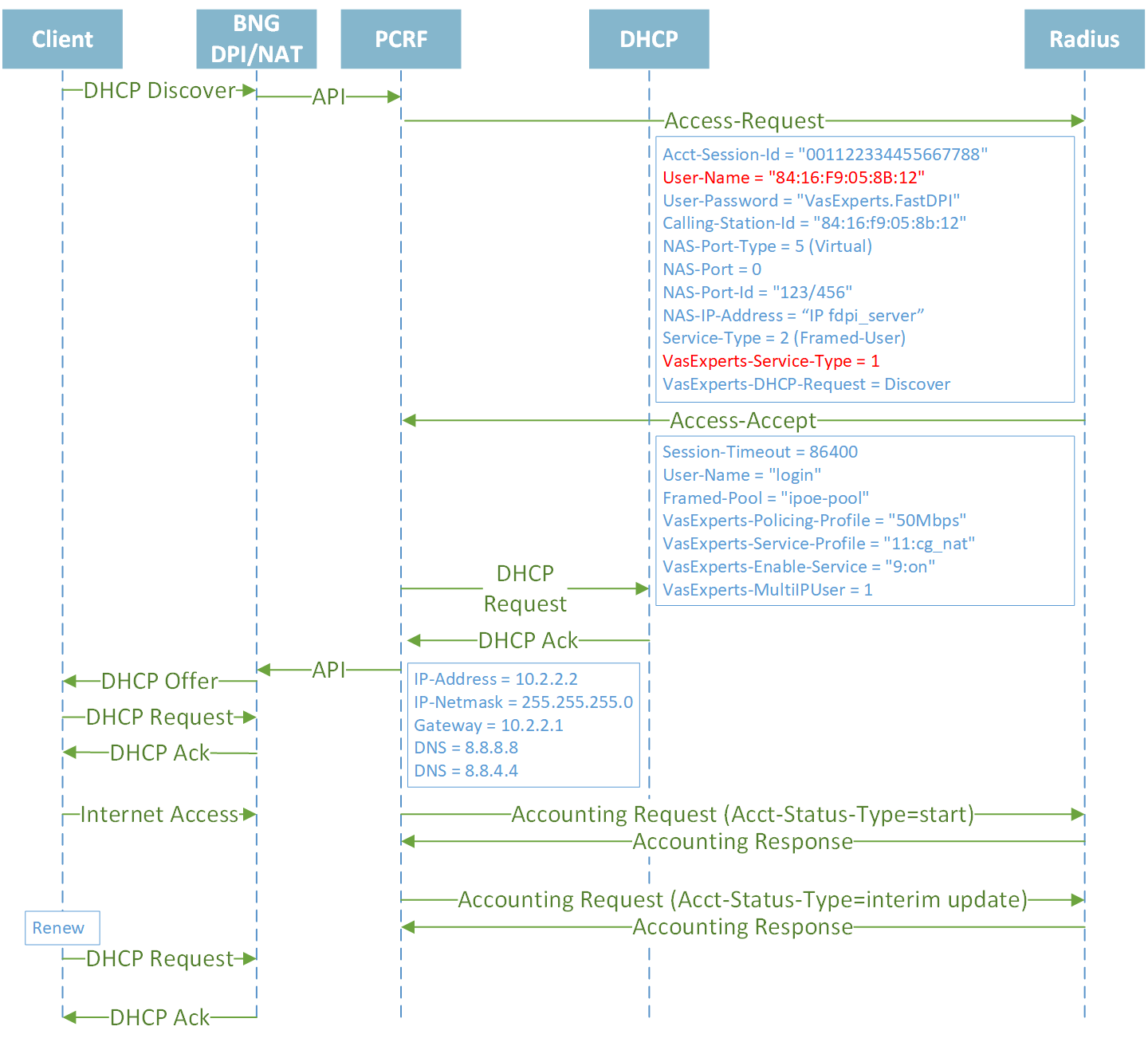
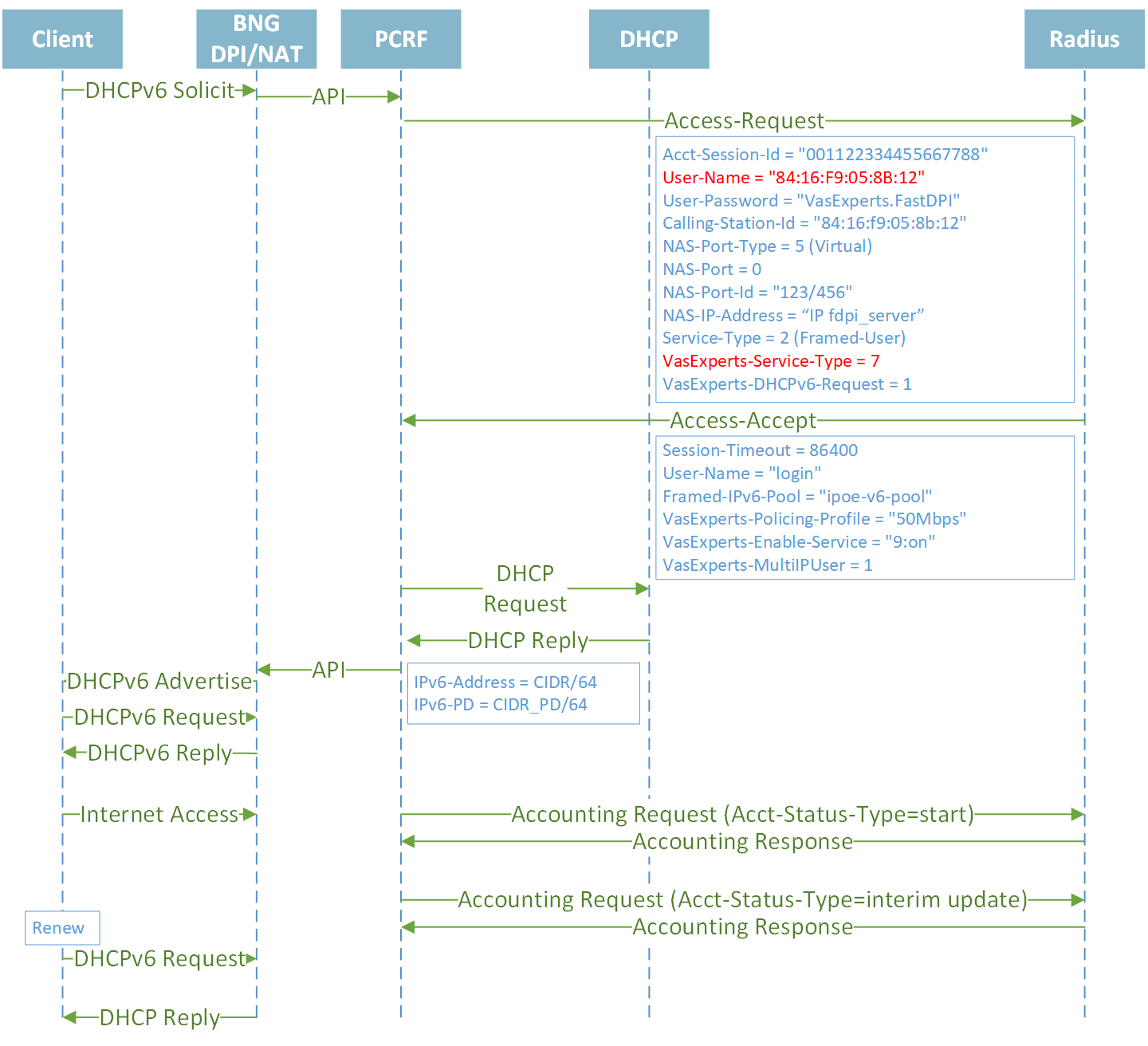
IPoE DHCP Dual Stack IPv4/IPv6
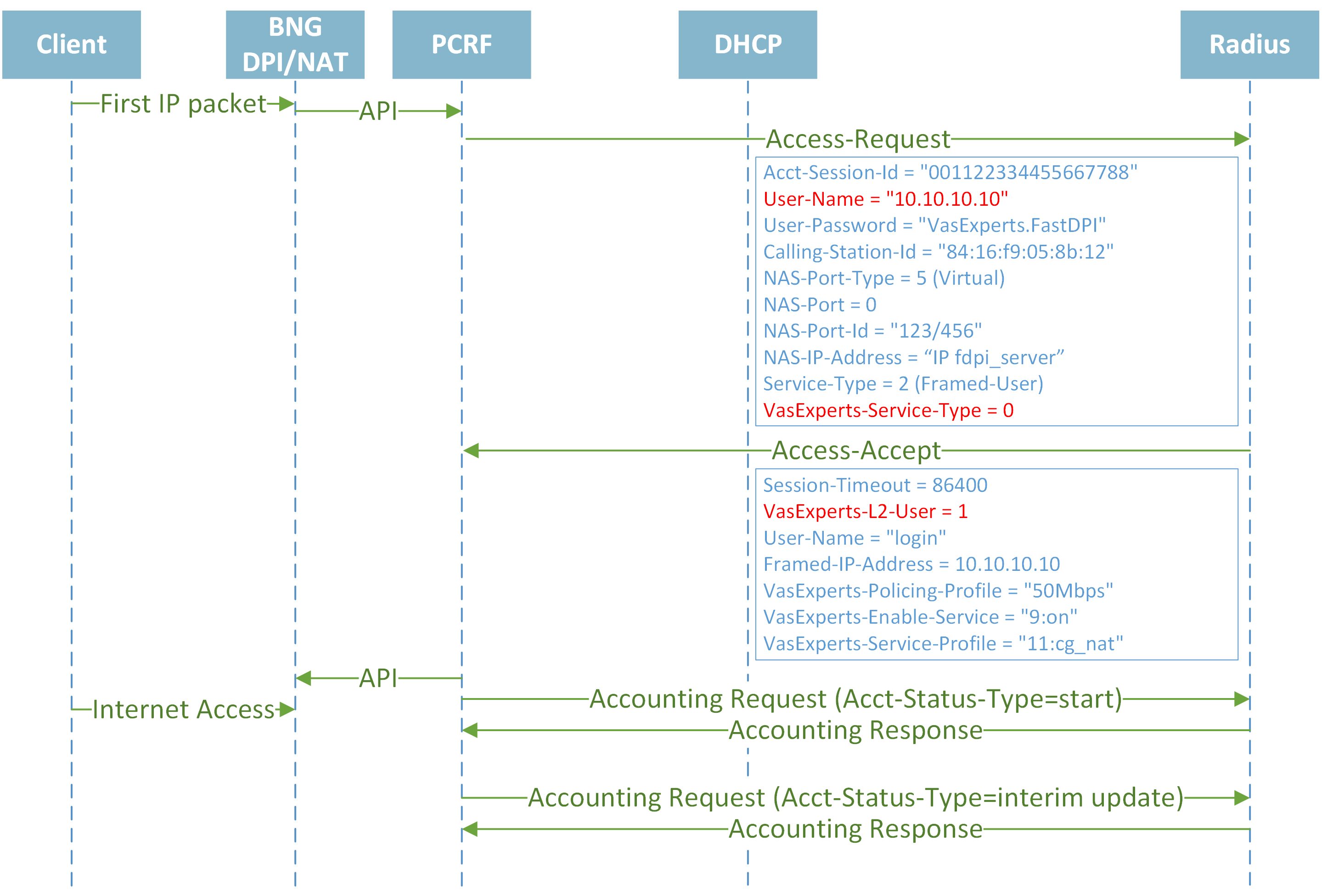
Establishing session IPv4
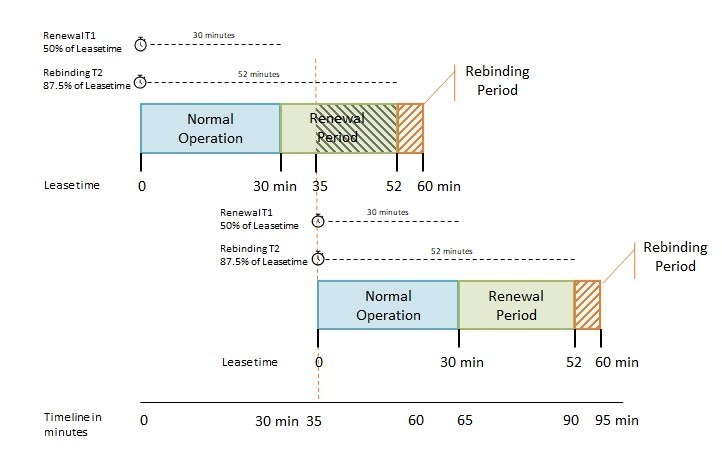
Understanding DHCP Renew and Lease Time
With a lease time one hour, the client will try to renew the lease after 30 minutes. At 35 min it contacts the DHCP server to extend/renew the lease. It’s granted so the timers reset, a new lease is acquired for another 60 minutes. In total, the IP Address is reserved for 95 minutes.
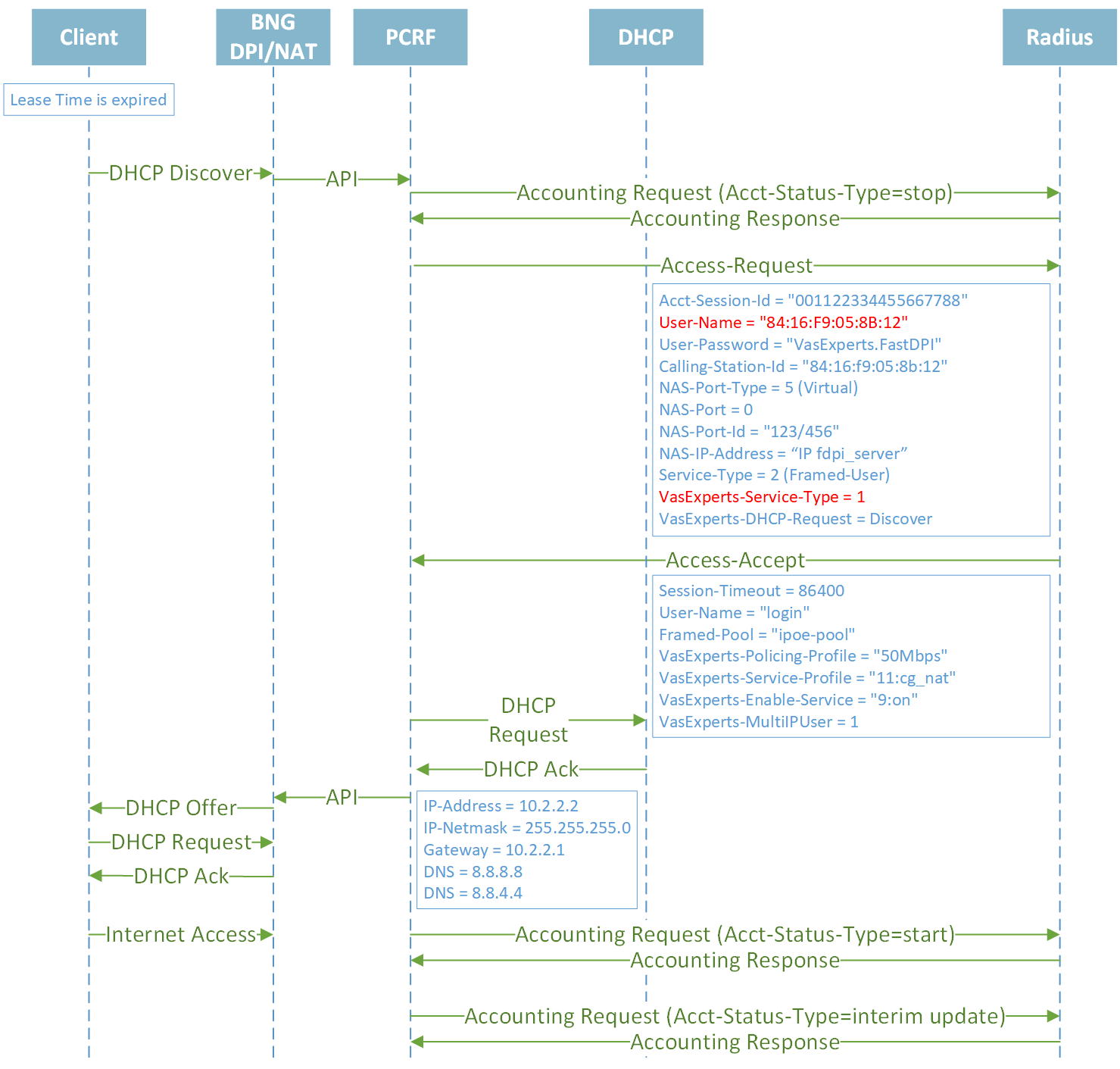
Closing session when Lease Time is expired and reauthorization
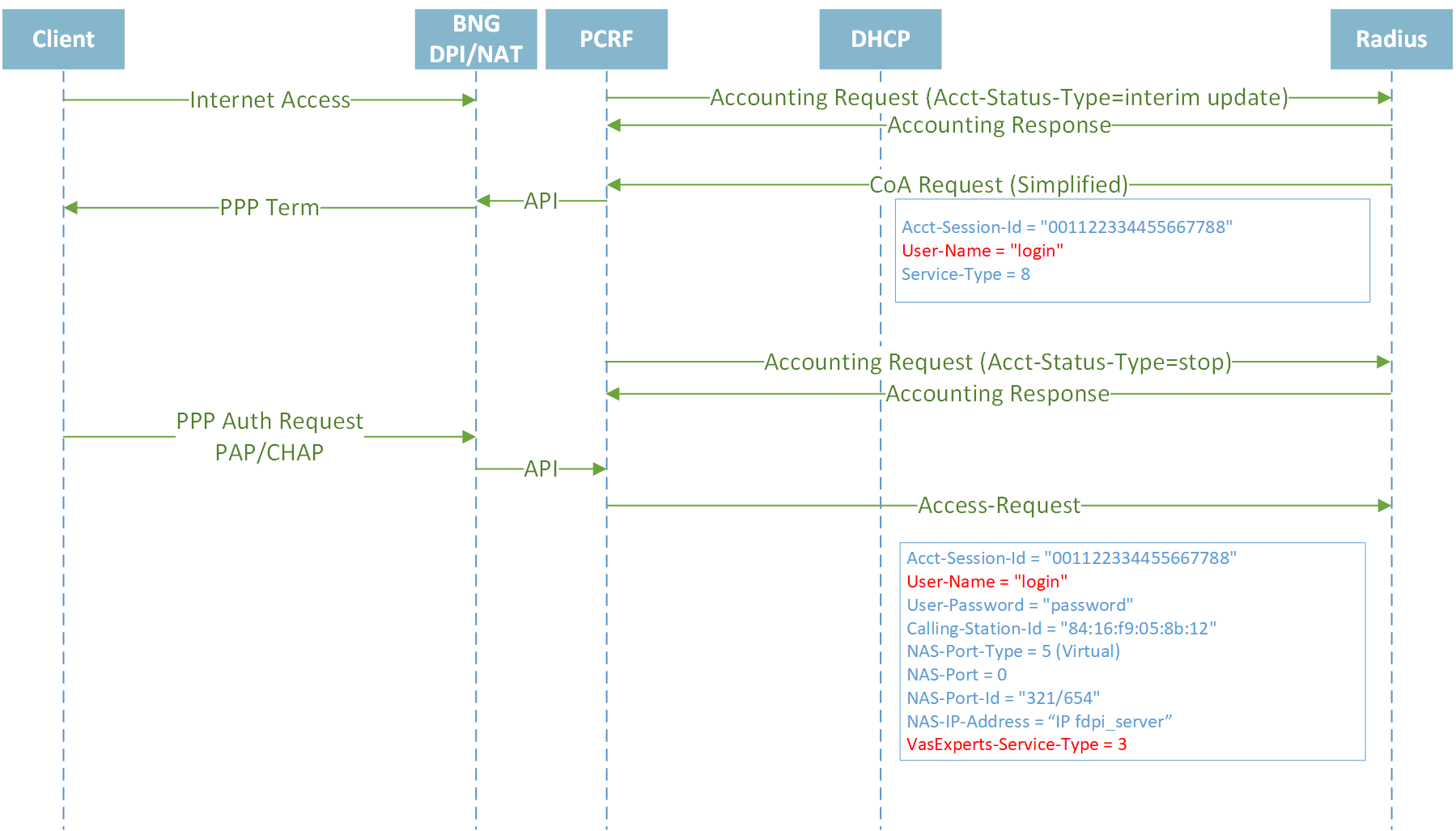
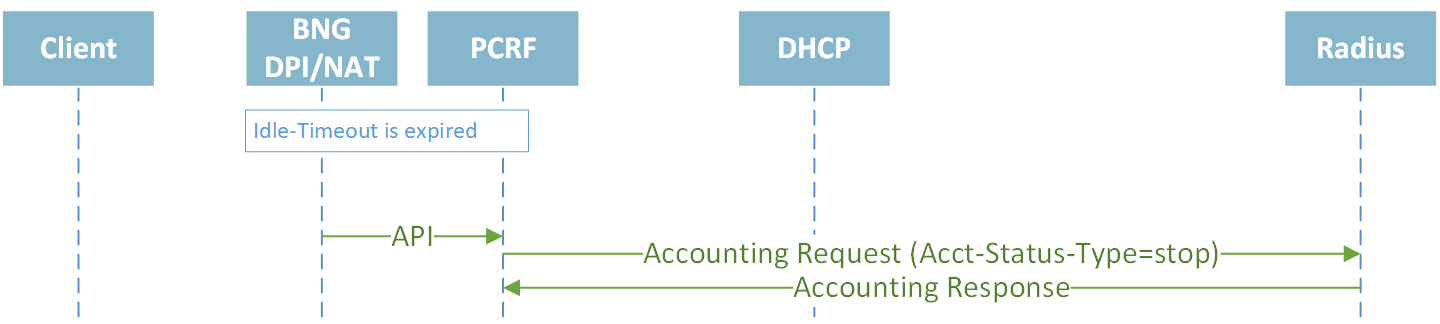
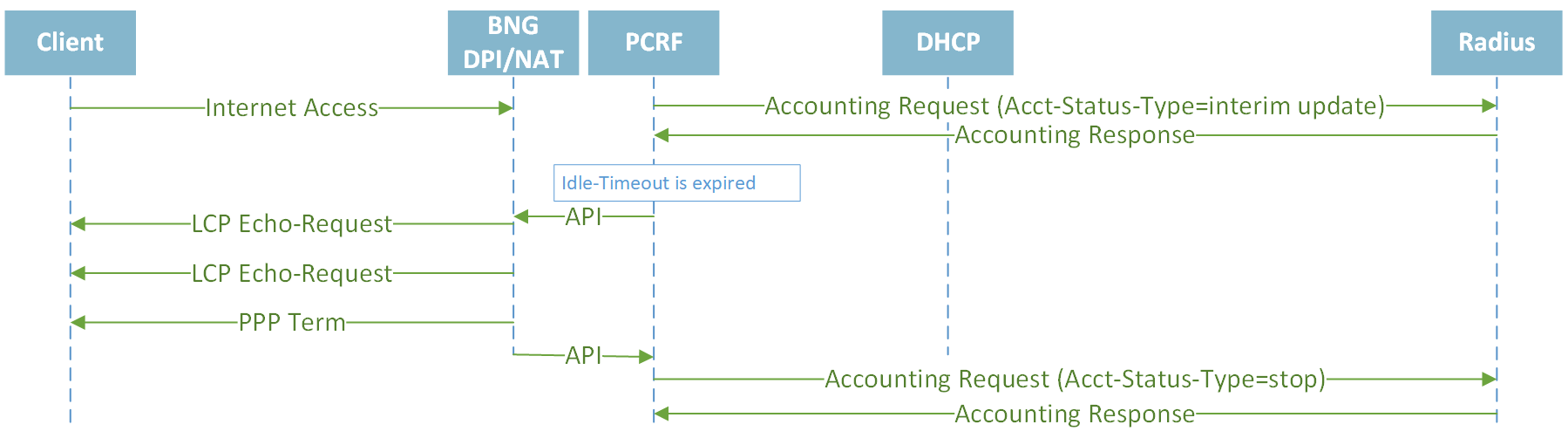
Closing session by Idle-Timeout
CoA with policing and services updates
Establishing session IPv6
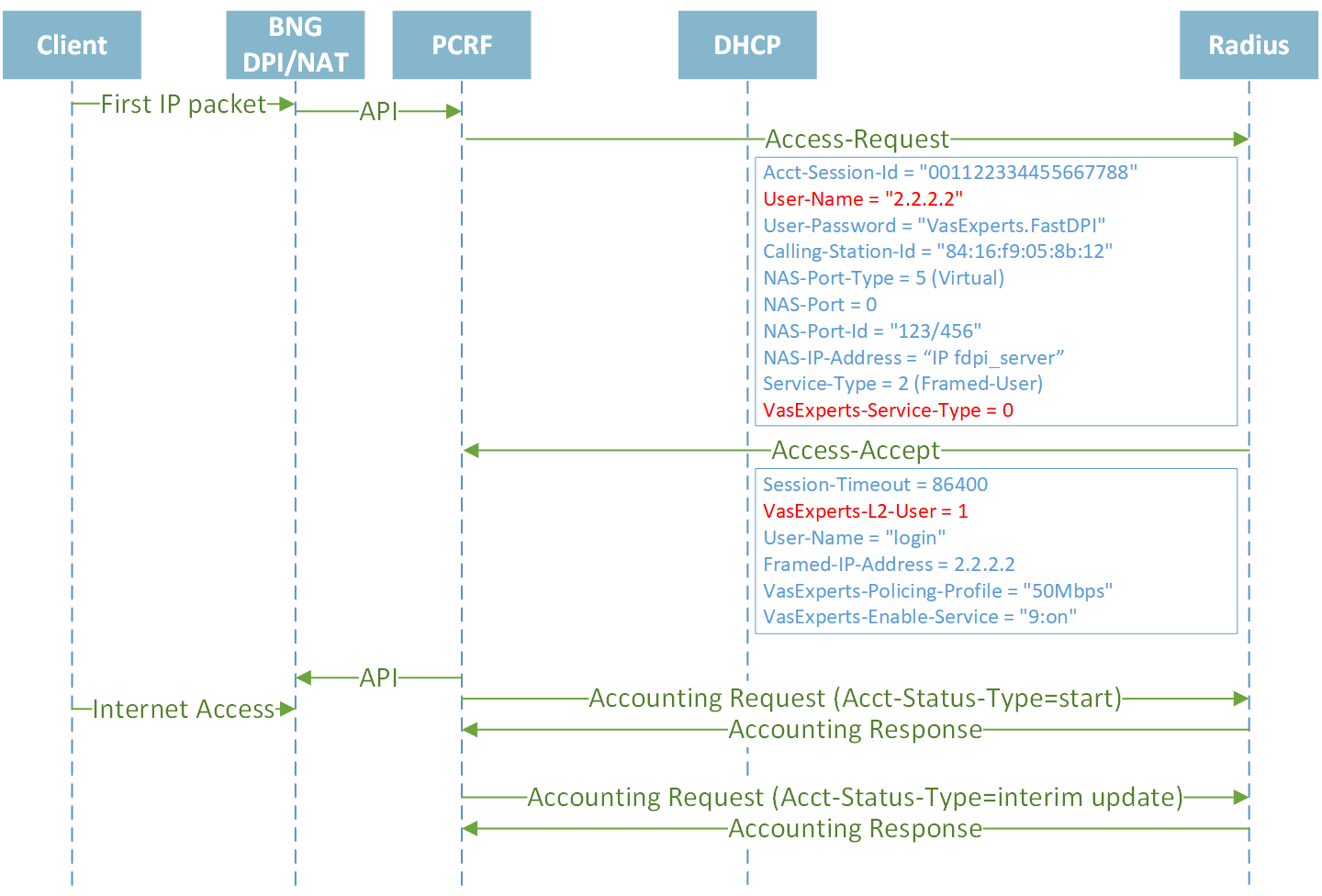
IPoE Statiс IPv4
Establishing session Public Statiс IPv4
Establishing session Private Statiс IPv4
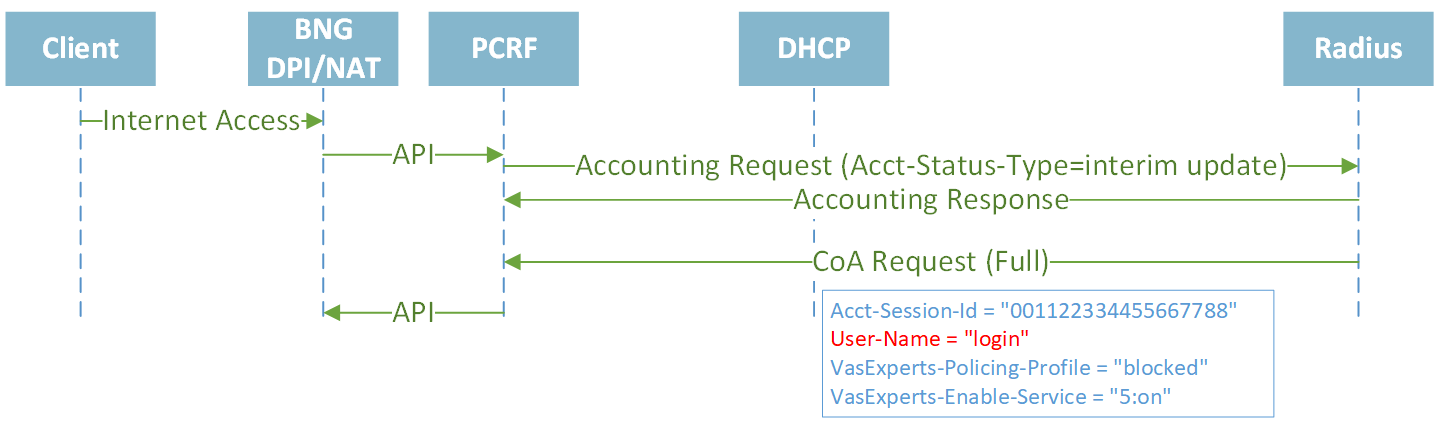
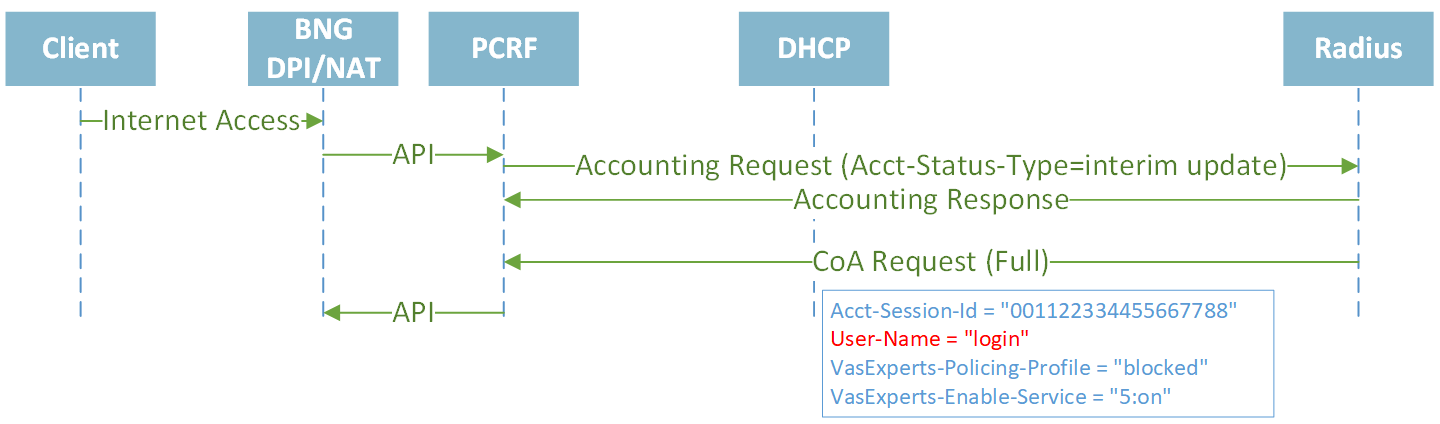
CoA with policing and services updates
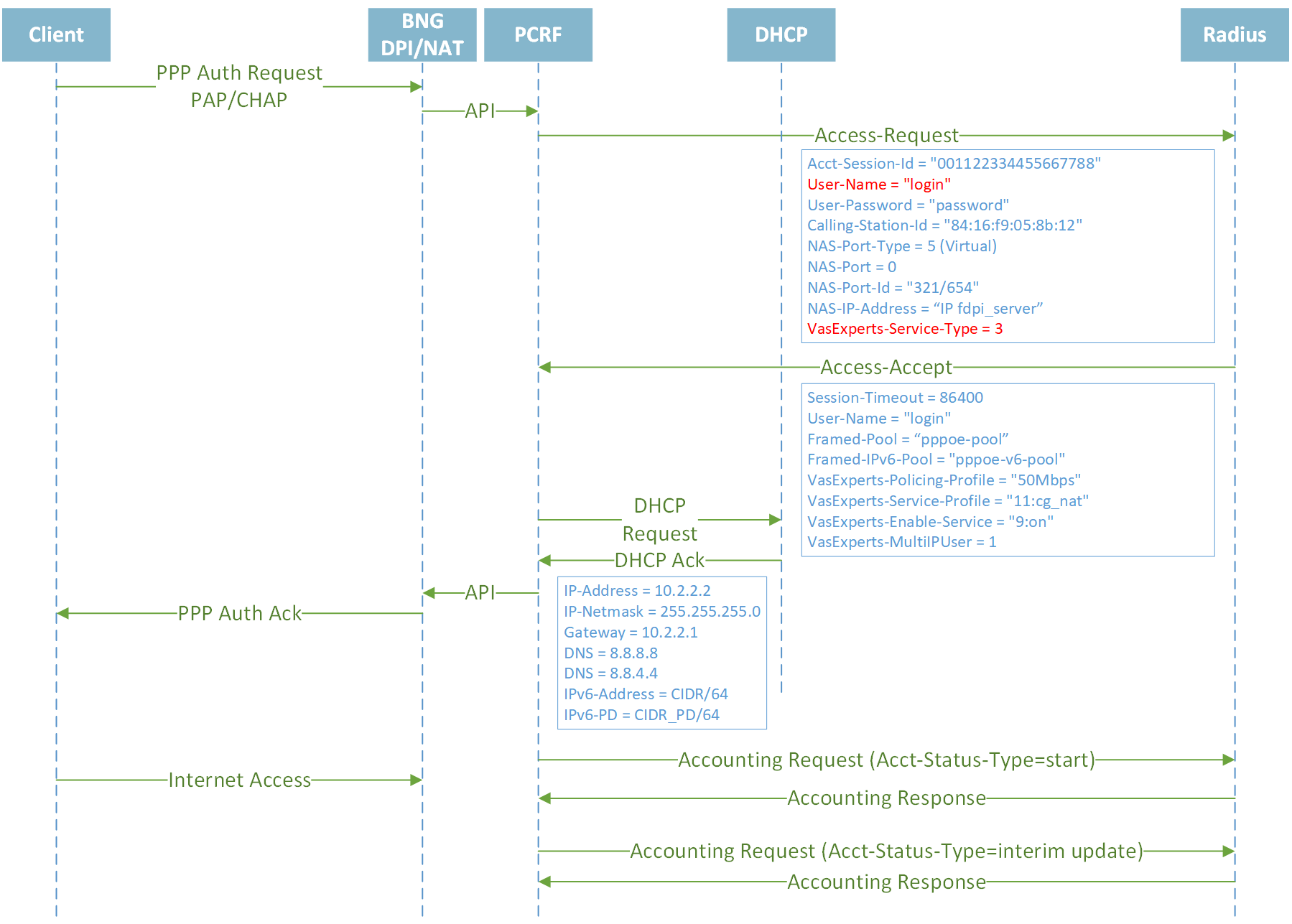
PPPoE Dual Stack IPv4/IPv6
Establishing session IPv4/IPv6
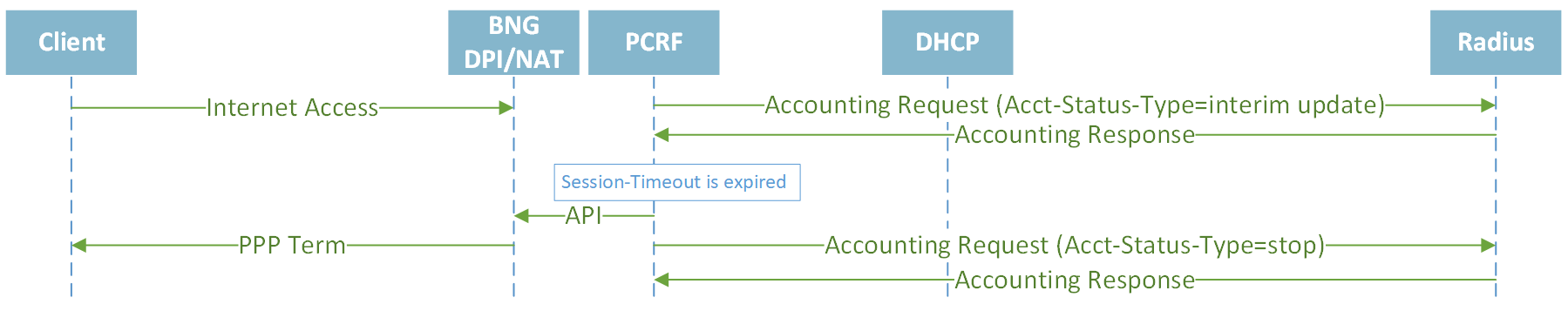
Closing session by Session-Timeout
Closing session by Idle-Timeout
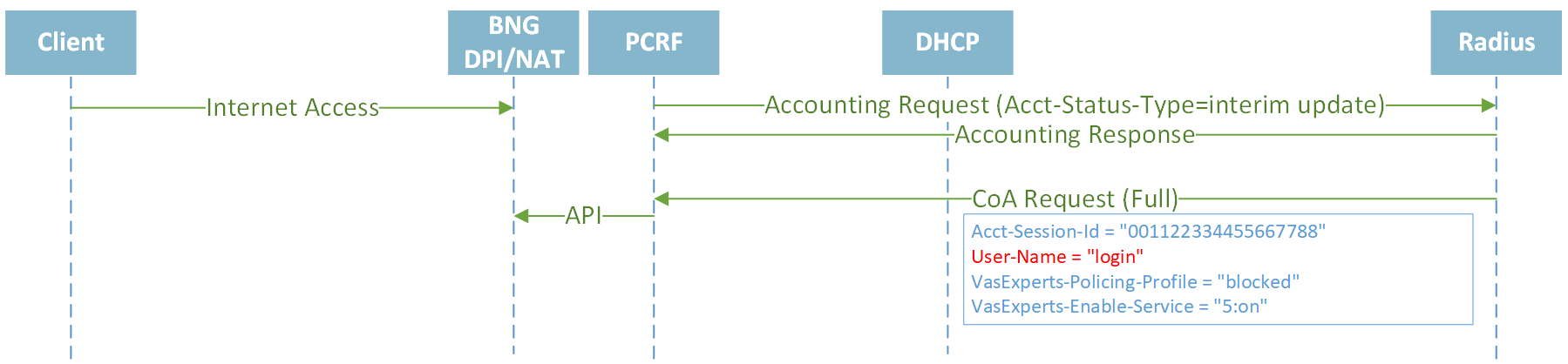
CoA with policing and services updates
CoA with PoD (Packet of Disconnect)