Internet Protocol (IP) is a unique numerical value assigned to devices connected to a network to facilitate communication.
This model still routes most Internet traffic but is on the verge of exhaustion. The address is made up of 32-bit integers expressed as hexadecimal notations. There is a total of approximately 4.3 billion IPv4 addresses.
A good example of an IPv4 address is 192.168.1.1.
IPV4 Components
IPv4 addresses are made up of the network and the host. The network and host are dependent on the prefix. Prefix=/16
Example of a Mask-255.255.255.0.0
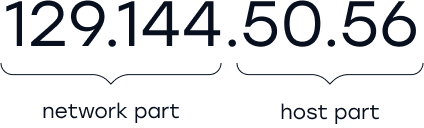
Network
This part represents a unique numeric identifier that is assigned to your network. Network class is identified by this part.
Host
The second part of the IPv4 address is assigned to hosts in your network. It is a unique hardware identifier. In every IP address existing in a network, the networking part is the same, but the host must be different.
Subnet Number:
This is an important part of a network, especially one with many hosts. In case you want to divide your network into subnets, it’s necessary to give them subnet numbers.
IPv4 Features and Characteristics
- 32-Bit address with numeric characters separated by dots
- It uses post address resolution protocol in mapping to mac address
- 12 header fields
- Contains Unicast, Multicast, and broadcast addresses style
- Manual assignment or through DHCP
IPv4 Pros and Cons
Pros
- Scalable and economic routing
- Significant network allocation
- IPv4 offers encryption to increase privacy and network security
- IPv4 addresses facilitate flawless encoding
- Specificity in communications, especially in multicast organizations
- Easy attachment of several devices across an oversized network
Cons
- IPv4 Addresses are on the verge of exhaustion
- High system management prices, complex, and slow. They are also labor-intensive
- Insufficient internet routing
- Non-obligatory security features