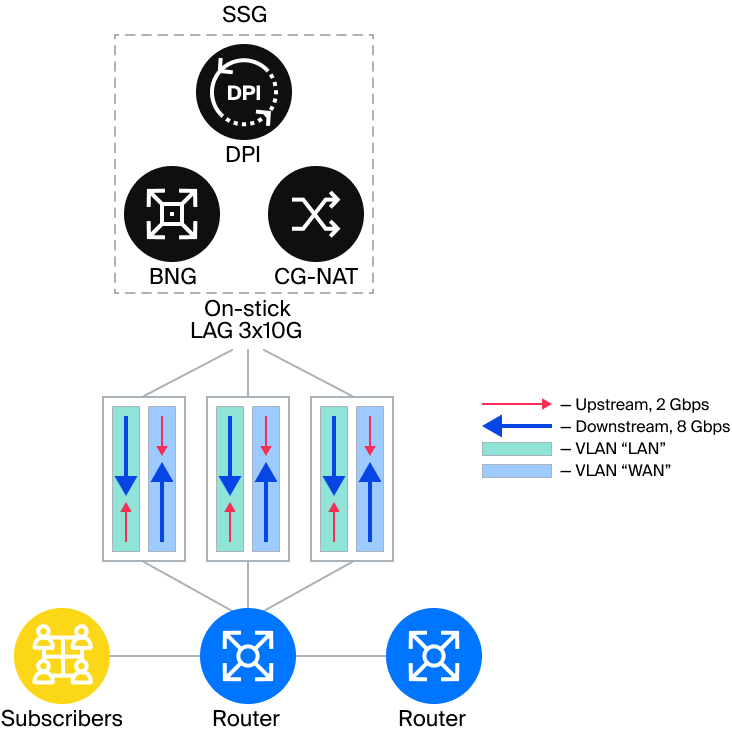
What is On-stick
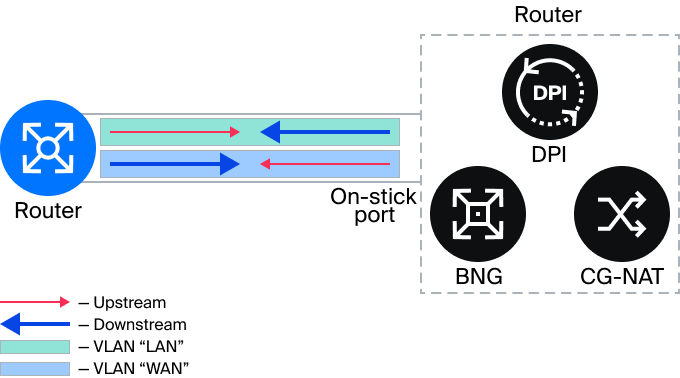
“Router-on-a-Stick” is a scheme for connecting physical ports with maximum link utilization, leveraging the asymmetry of Downstream and Upstream traffic. In fact, the Stingray Service Gateway is connected ‘on-a-stick’ to the core router through multiple physical links with VLAN separation between WAN and LAN. This allows businesses to realize significant cost savings as their traffic and subscriber base grow. Previous versions of the SSG only supported the inline mode, where router ports were often used inefficiently. With the introduction of On-Stick, service providers have the opportunity to increase the throughput capacity of the network core.
What are the differences between Inline and On-Stick modes?
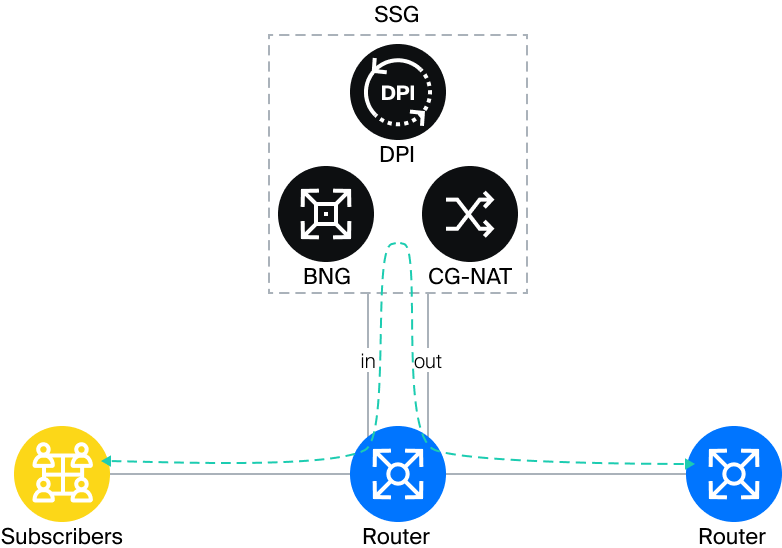
Inline involves plugging a device into a gap in the active links of one router
or between two different routers.
In this case, two ports per link are utilized to connect the device on the routers:
- LAN, which is located on the subscriber side;
- WAN, which is located on the Internet side.
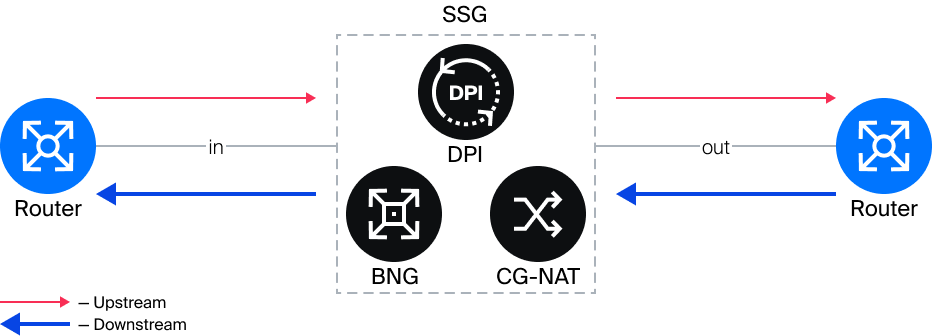
One of the problems with Inline mode is that router ports are not evenly utilized. The traffic flow that goes to the subscribers (Downstream) is usually greater than the traffic that goes to the Internet (Upstream). Therefore, ports are maximally utilized in one direction and minimally utilized in the opposite direction.
To eliminate the asymmetry in router port utilization during Inline mode of operation, Onstick mode was developed. Onstick allows WAN -> LAN and LAN -> WAN traffic to be transmitted through a single device port.
What is the advantage of On-stick
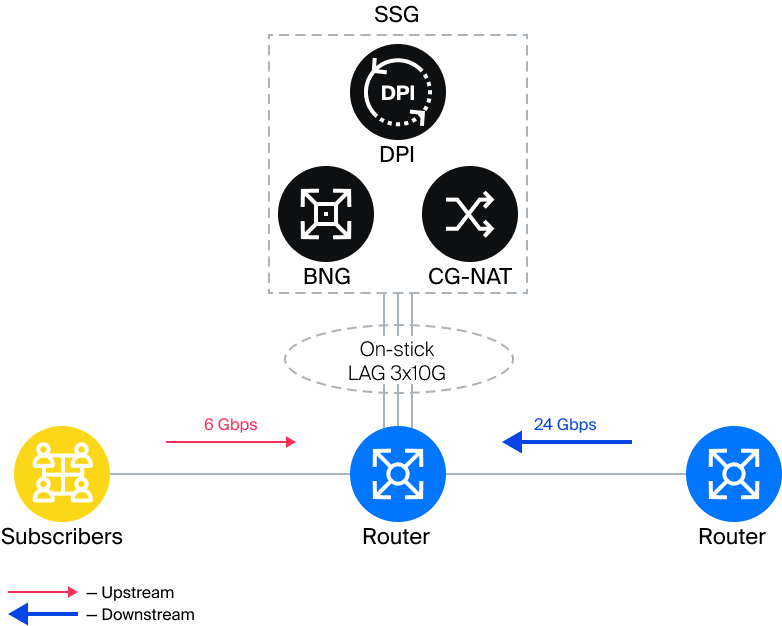
The image shows that when Onstick mode is connected, asymmetry disappears and the router ports are utilized evenly. Upstream traffic is 25% of Downstream traffic. Therefore, On-stick is always a more economical solution, regardless of the amount of Downstream traffic and usage scenario.
Example
If the Downstream traffic is 24 Gbps during the peak hours, then:
- in Inline mode, 6x10G ports on the routers will be utilized for its transmission: 3x10G for LAN connection and 3x10G for WAN. Upstream traffic that goes through the router ports will be 6 Gbps, and the resources allocated for it will be designed to carry 30 Gbps of traffic.
- In Onstick mode, only 3 ports on the router will be required to carry the same amount of traffic.
It is recommended to aggregate ports in On-Stick mode into a single LAG logical link. Since version 13, the SSG supports LAG/LACP with multiple balancing mechanisms. You can find more details in our documentation: wiki.vasexperts.com/dpi_onstick